16 minute read · December 11, 2023
Virtual Data Marts 101: The Benefits and How-To

· Senior Tech Evangelist, Dremio

The concept of data marts has long been a pivotal strategy for organizations seeking to provide specialized access to critical data for their business units. Traditionally, data marts were seen as satellite databases, each carved out from the central data warehouse and designed to serve specific departments or teams. These data marts played a vital role in enhancing data access and decision-making but came with challenges.
Challenges of Traditional Data Marts
Traditional data marts, while valuable, often came with a price tag that extended beyond financial costs. Creating and maintaining these data silos involved the cumbersome task of copying data. This not only led to issues of data duplication but also incurred significant storage costs. Additionally, data movement expenses mounted as data needed to be synchronized between the central warehouse and these data marts.
These challenges became increasingly evident in the era of big data and distributed data sources, where data volume, variety, and velocity surged. The traditional approach of copying data into separate data marts needed help in order to keep pace with the demands of modern data analytics.
Introducing "Virtual Data Marts" with Dremio
Enter Dremio, a transformative force in the world of data. Dremio's semantic layer, with its ability to create virtual data marts, offers a paradigm shift in how organizations can harness and manage their data assets. The concept is elegantly simple yet profoundly impactful: Why copy data when you can access and govern it virtually?
In this comprehensive guide, we'll embark on a journey into the "Virtual Data Marts" realm, uniquely enabled by Dremio's semantic layer and data reflections, allowing not just for virtualization but virtualization at scale. We will explore how this innovative approach eliminates the need for copying data, drastically reduces storage costs, and minimizes data movement expenses. The virtual data mart concept promises significant cost savings and enhances data governance, agility, and security.
The Drawbacks of Traditional Data Marts
The traditional approach of moving data from your data lake into a data warehouse platform and then modeling your warehouse across several data marts has some challenges we will explore.
Understanding Traditional Data Marts
Before diving into the drawbacks of traditional data marts, let's briefly explore what data marts are. Traditional data marts are subsets of a central data warehouse designed to serve the specific analytical needs of departments, teams, or business units. They typically contain a subset of the data available in the central data warehouse and are structured to facilitate specific types of analysis. These subsets are often physical copies and variations of the original datasets, creating more unique versions of the data to update and keep consistent manually.
The Limitations of Traditional Data Marts
While traditional data marts have been instrumental in enhancing data access for decision-makers, they come with a set of limitations that have become increasingly evident in today's data-driven landscape.
Data Duplication and Synchronization Issues
- One of the fundamental challenges of traditional data marts is data duplication. When data is copied from the central data warehouse into these marts, it leads to multiple versions of the same data. This data duplication not only consumes additional storage but also introduces synchronization complexities.
- Maintaining data consistency between the central warehouse and the diverse data marts demands meticulous synchronization endeavors, which are prone to errors and time-consuming. Inconsistent data scattered across distinct marts can give rise to disparities in analytical outcomes, undermining trust in data-driven decision-making. These data consistency issues reverberate beyond data quality, extending to potential costly blunders in decision-making procedures.
- The ramifications of these data copies ripple through the operational landscape, saddling organizations with heightened overheads, diminished productivity for data engineers, data drift, escalated costs, elevated security vulnerabilities, and increased compliance risks. However, these are just the IT-centric challenges; business-related hurdles compound the complexity.
- Whenever business requirements evolve, or fresh inquiries arise, the process of addressing them can stretch into weeks, leading to frustration for business analysts, data engineers, data architects, and IT/analytics leaders.
Increased Storage Requirements
- Traditional data marts necessitate storing data separately from the central warehouse. This approach increases storage requirements as each mart accumulates its copy of data. As data volumes grow, so do storage costs, making it a significant financial burden for organizations.
Financial Implications
The limitations of traditional data marts have far-reaching financial implications for organizations:
Increased storage costs: The need to store multiple copies of data in various data marts significantly inflates storage costs. Organizations are forced to allocate substantial budgets for additional storage infrastructure and maintenance.
Data movement expenses: Keeping data synchronized between the central warehouse and data marts entails data movement expenses. These include data transfer fees, network usage charges, and computational resource allocation for data copying and transformation.
Resource allocation: The manpower and resources required to manage data duplication, synchronization, and data quality across multiple data marts can strain an organization's budget and divert valuable resources from other critical initiatives.
Risk of cost overruns: Inconsistent data and data quality issues can lead to costly errors or misinformed decisions, potentially resulting in financial losses or missed opportunities.
As organizations strive to optimize their data infrastructure, it becomes increasingly clear that the drawbacks of traditional data marts extend beyond mere operational challenges. They carry substantial financial burdens that can hinder budget efficiency and limit the agility needed to respond to rapidly evolving business requirements. In the following sections, we'll explore how "Virtual Data Marts" powered by Dremio's semantic layer provides a compelling solution to these challenges, offering cost-effective, agile, and efficient data mart alternatives.
Introduction to Dremio's Semantic Layer
Dremio's semantic layer is key to what makes the Dremio approach unique, making ease of use and performance things that go hand in hand instead of being a trade-off. Dremio enables "Virtual Data Marts," a paradigm that addresses the challenges of traditional data marts while unlocking many benefits. While traditional data marts allow you to model your warehouse across multiple business lines or domains through layers of physical copies, Dremio allows you to achieve the same modeling across business units through layers of no-copy virtualization.
The Game-Changer: Dremio's Semantic Layer
In the past, other platforms promised to simplify data management processes through virtualization. However, they often needed help scaling up due to performance limitations, which still needed complex layers of copies, materialized views, extracts, and cubes. However, Dremio takes a different approach by leveraging Apache Arrow-based processing and data reflections.
With Apache Arrow providing a fast in-memory format for data processing, Dremio can swiftly handle data from various sources right out of the gate, delivering high-speed performance. Meanwhile, using reflections provides further performance optimization to enable additional scale. Reflections provide the same optimization capabilities that would typically demand complex sequences of data pipelines, materialized views, extracts, and cubes, which come with the burden of fragile maintenance and synchronization tasks.
By eliminating these performance bottlenecks, Dremio's semantic layer empowers you to model and govern your data virtually across logical views. This breakthrough approach sets Dremio apart for simplified and efficient data management.
Benefits of Virtual Data Marts
The advantages of virtual data marts are manifold, offering a compelling case for organizations to adopt this approach:
Elimination of data copying and synchronization: Virtual data marts powered by Dremio eliminate the need for data duplication and synchronization. Data is accessed directly from the central data warehouse or source, ensuring data consistency and integrity.
Cost savings on storage and data movement: Storage costs are significantly reduced with no data copying into separate data marts. Moreover, eliminating data movement expenses, including data transfer fees and network usage charges, leads to substantial cost savings.
Enhanced data governance and security: Data governance becomes more straightforward and effective as data remains centralized and under strict governance control. Security measures are applied consistently across the data infrastructure.
Improved agility in responding to changing business needs: Virtual data marts provide the agility to respond quickly to evolving business requirements. Data can be modeled and remodeled on the fly, ensuring that analytical insights remain aligned with business demands.
Application of Virtual Data Marts with Dremio
The application of virtual data marts has become a game-changer for organizations seeking to harness the full potential of their data assets. Let's walk through how a company can leverage Dremio to create and manage virtual data marts, empowering users with data access and acceleration capabilities.
1. Folder creation for business units:
- A Dremio administrator initiates the process by creating a folder structure within Dremio's user interface, mirroring how data marts are traditionally established in a data warehouse.
- Each folder corresponds to a specific domain, business unit, department, or team. This organizational structure streamlines data access and ensures users can easily locate and interact with their respective data.
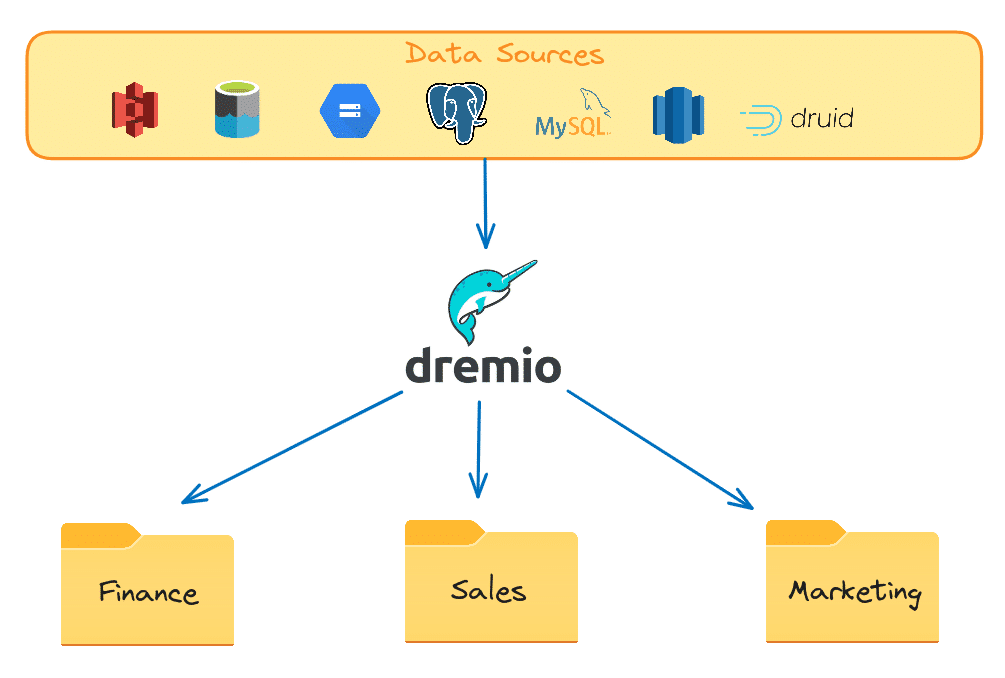
2. Data source integration and view creation:
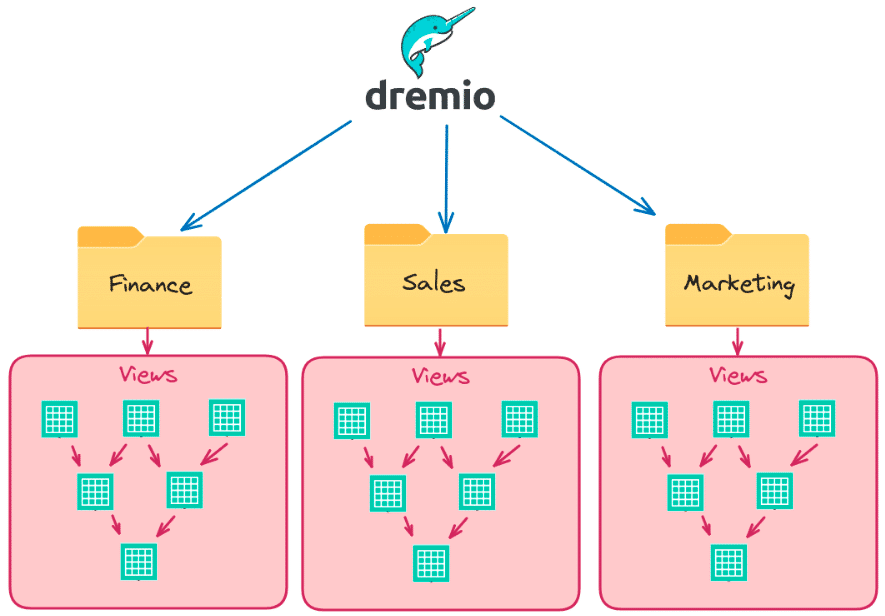
- Dremio's connectivity capabilities enable the administrator to seamlessly connect to various data sources, including databases, data lakes, and cloud storage.
- The administrator creates views within each folder that logically represent the underlying data sources. These views can include any necessary transformations, aggregations, or masking policies to control data access and protect sensitive information.
- For views that require high query performance, the administrator can enable raw reflections to accelerate complex queries efficiently. Similarly, views designed for BI dashboards can have aggregate reflections enabled, providing users with sub-second BI dashboard performance.
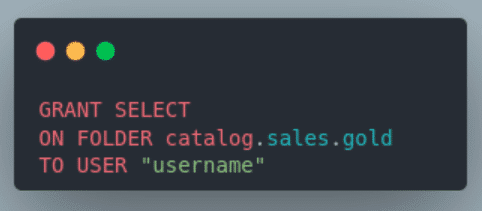
3. Access control and permissions:
- Dremio's robust access control mechanisms allow the administrator to assign different access levels to users and roles for each folder and view.
- Granular control over who can access, view, or modify the data ensures that sensitive data remains protected while also enabling data democratization.
- By tailoring permissions, administrators can empower users with the right level of access to perform their tasks effectively.
4. User-curated data and data mesh approach:
- Dremio goes beyond traditional data mart management by allowing users to connect their datasets and curate data within their designated folders.
- This capability aligns with the data mesh approach, where data ownership and curation are distributed across business units or teams.
- Users can blend their curated data with existing organizational datasets, fostering collaboration and ensuring data remains relevant to specific use cases.

5. User-friendly interface and automation:
- Dremio provides an intuitive user interface where administrators can perform all these tasks through point-and-click actions or SQL queries.
- Additionally, automation options are available through the Dremio REST API, Apache Arrow Flight, or ODBC/JDBC connections, streamlining administrative processes and ensuring consistency across virtual data marts. This can even be further enhanced with Dremio’s rich tapestry of integrations such as Dremio’s DBT integration that makes consistently modeling your virtual data marts manageable at the largest scales.
By adopting Dremio's approach to virtual data marts, organizations can create a flexible, agile, and secure data environment that caters to the unique needs of different business units. The ability to apply row-level masking, control query performance with reflections, and allow user curation fosters collaboration, accelerates data-driven decision-making, and aligns with modern data management principles. Dremio empowers organizations to make data-driven insights more accessible and valuable.
Conclusion
The concept of data marts has undergone a remarkable transformation. Traditionally, data marts were seen as satellites of the central data warehouse, each with its own challenges, including data duplication, synchronization issues, and substantial financial burdens.
However, with the introduction of "Virtual Data Marts" powered by Dremio's semantic layer, organizations now have a revolutionary solution to these challenges. This transformative approach eliminates the need for data copying, significantly reduces storage and data movement costs, enhances data governance and security, and empowers organizations to respond with agility to evolving business needs.
Administrators can efficiently manage virtual data marts by creating folder structures for business units, integrating various data sources, optimizing performance with data reflections, and crafting views with fine-grained access control. Users, in turn, benefit from sub-second query performance, the ability to curate their datasets, and the flexibility to connect their data, following the principles of a data mesh approach.
Dremio's user-friendly interface and automation options simplify the process, making the transition to virtual data marts seamless and efficient.
As organizations continue their journey in data management, adopting virtual data marts with Dremio's semantic layer represents a significant step forward. It's a leap toward a data landscape that is cost-effective, agile, and secure — a landscape where data access and acceleration are streamlined and insights are within reach for all who need them.
The age of virtual data marts has arrived, promising improved data management, more informed decision-making, and a brighter future for data-driven organizations.
Presentation: ZeroETL and Virtual Data Marts
Blog: Building a Lakehouse on Your Laptop



