8 minute read · October 9, 2025
Why Dremio Outperforms Redshift: Query Speed, Concurrency, and Cost Efficiency Without Limits
The Shift from Warehouses to the Agentic Lakehouse
Amazon Redshift has long been a dependable data warehouse for analytics, but the analytics landscape has evolved. Organizations are no longer just running dashboards—they’re powering agentic AI systems that reason, act, and make autonomous decisions based on live business data. These workloads demand real-time responses, high concurrency, and open data access—requirements that Redshift’s closed, cluster-based architecture struggles to meet.
As queries slow under pressure and scaling requires manual tuning, the cost and complexity of maintaining performance grow exponentially.
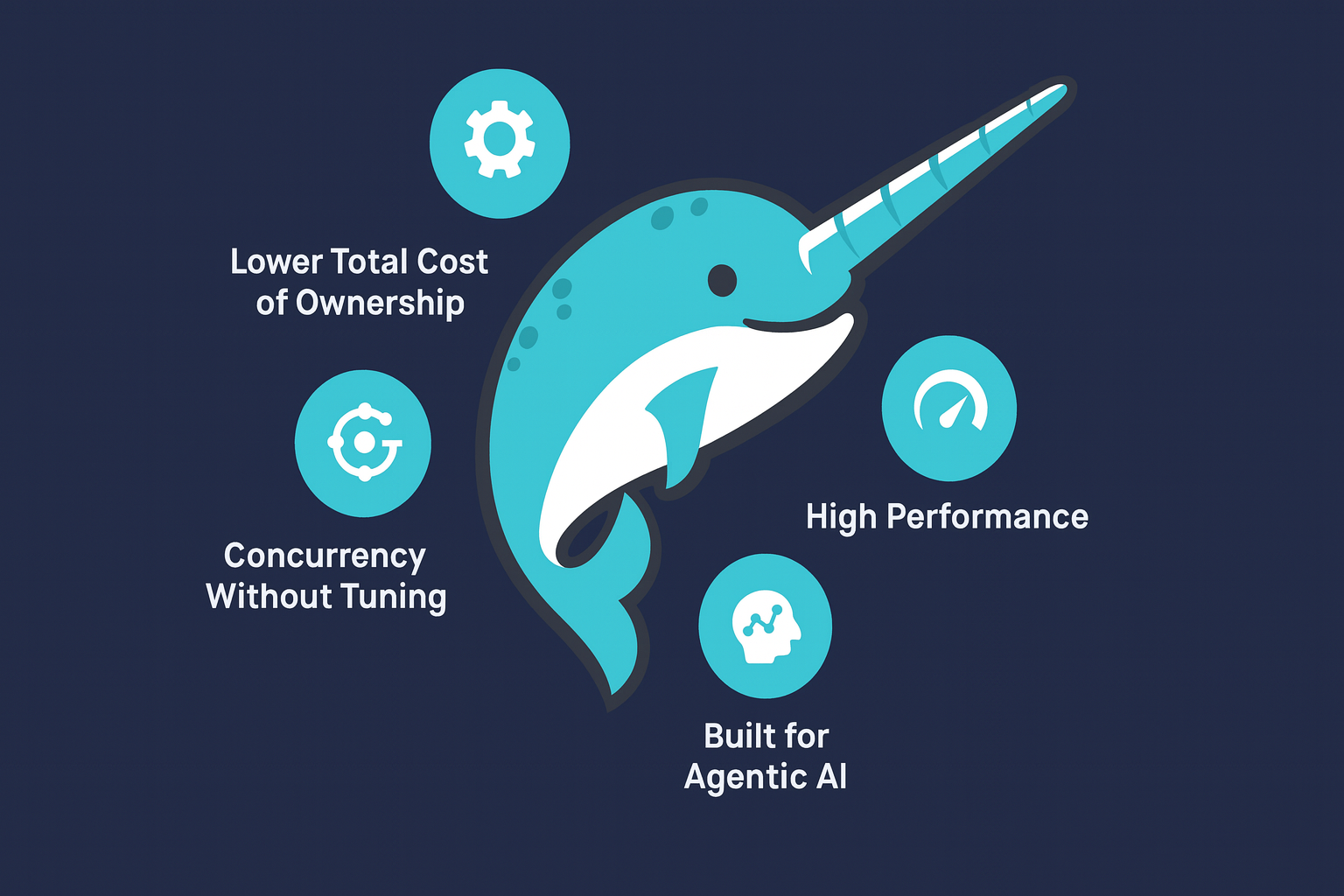
Dremio's Agentic Lakehouse represents a new paradigm: a lakehouse designed from the ground up for the AI era. Built on an open, Iceberg-native foundation and powered by a next-generation Apache Arrow query engine, Dremio combines autonomous acceleration, elastic concurrency, and AI-ready semantic layer to deliver speed, scale, and efficiency for modern, agent-driven analytics.
Redshift’s Bottlenecks in the Modern Era
For many organizations, Redshift delivers good performance at the start. But as datasets grow and usage scales, pain points quickly surface. Queries take longer to return results, and concurrency requires constant management through workload queues and cluster resizing. Data must be copied into proprietary Redshift clusters, introducing ETL complexity, duplication, and lock-in. And with compute running around the clock, customers pay even when queries aren’t running. Achieving acceptable performance often requires hours of manual tuning—managing sort keys, distribution keys, and vacuuming jobs.
These limitations don’t just slow down data teams—they slow down the business. In today’s environment, where decisions are powered by agentic AI and real-time analytics, waiting minutes for queries or being forced to ration concurrency isn’t good enough.
Try Dremio’s Interactive Demo
Explore this interactive demo and see how Dremio's Intelligent Lakehouse enables Agentic AI
Why Dremio Runs Faster
Dremio delivers performance by eliminating the bottlenecks that slow down traditional warehouses. At the core of Dremio’s performance advantage is Autonomous Reflections, an intelligent acceleration layer that automatically optimizes queries across all workloads. Unlike Redshift’s materialized views, which require manual creation and maintenance, Reflections are created, tuned, and retired automatically. They adapt to query patterns and data freshness needs in real time, ensuring sub-second response times even on multi-terabyte datasets.
Under the hood, Dremio’s Apache Arrow–based SQL engine executes queries in a vectorized, in-memory fashion. This means data is processed in highly efficient batches directly in memory, minimizing CPU overhead and drastically reducing latency. Dremio also supports Apache Iceberg natively, allowing users to query massive datasets directly in object storage without ingesting or duplicating data. Iceberg’s advanced metadata model provides capabilities like snapshot isolation, partition pruning, and schema evolution, ensuring queries are both fast and accurate across complex datasets.
Dremio’s performance edge is further amplified by its Columnar Cloud Cache (C3). Frequently accessed data is cached locally, close to compute, in a columnar format. This architecture reduces I/O bottlenecks and network hops, leading to lightning-fast query times even as data scales into the petabyte range. Together, these technologies enable enterprises to run analytics workloads that are not only faster than Redshift but also far more efficient—making Dremio the ideal platform for AI-driven and agentic workloads that depend on real-time access to knowledge.
Concurrency Without Tuning
As data adoption grows across the enterprise, concurrency becomes a critical bottleneck in Redshift. Traditional data warehouses require administrators to carefully manage workload queues, reserve cluster slots, or spin up additional clusters just to keep queries from stalling. The result is operational complexity and unpredictable performance.
Dremio takes a fundamentally different approach. Its elastic query engines automatically scale up and down based on demand. When hundreds or even thousands of users issue queries simultaneously—whether through BI dashboards, SQL editors, or AI agents—Dremio dynamically provisions resources to maintain consistent performance without contention. When activity subsides, engines gracefully scale back to zero, eliminating wasted compute and reducing costs.
This elasticity also extends across workloads. Different teams or applications can operate in isolated query engines, ensuring one group’s heavy workload doesn’t impact another’s performance. The result is a self-optimizing environment where concurrency just works—no manual queue management, no slot tuning, and no guessing how much capacity is enough.
Lower Total Cost of Ownership
Performance at scale means little if costs spiral out of control. Redshift’s pricing model, based on always-on clusters and duplicated data pipelines, leads to inefficiencies that compound as data grows. Dremio’s architecture was designed to reverse that dynamic.
Because Dremio queries data in place—directly from cloud object storage—there’s no need to copy or ingest data into proprietary storage. This eliminates ETL duplication, reduces storage redundancy, and removes the operational overhead of maintaining ingestion pipelines. Its on-demand compute model means you only pay for resources when queries are actively running, not when clusters are idle.
Customers consistently report 50–70% lower total cost of ownership (TCO) compared to Redshift, driven by reduced infrastructure, fewer manual operations, and the ability to consolidate analytics, AI, and data engineering workloads on a single open platform. With Dremio, teams spend less time tuning systems and more time generating insight that moves the business forward.
Built for the Agentic AI Future
Where Redshift was built for static dashboards, Dremio was built for Agentic AI—a world where intelligent agents, large language models, and data-driven systems need governed, context-aware access to data.
At the heart of this capability is Dremio’s unified semantic layer, which provides a consistent, governed view of business data across all sources. This layer allows AI agents and analysts alike to interpret data with full business context, transforming raw data into structured, explainable knowledge.
Beyond analytics, Dremio’s Model Context Protocol (MCP) Server integration connects directly with AI systems like Claude, Gemini, and GPT. This means AI agents can securely query governed data through standardized endpoints, respecting access policies and data lineage. Dremio’s Enterprise Iceberg Catalog (powered by Apache Polaris) further ensures AI workloads operate on consistent, trusted metadata across hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
Together, these capabilities form the foundation of the Dremio Agentic Lakehouse—a platform that unifies data, analytics, and AI so agents can reason, decide, and act at machine speed.